Document Actions reference
Add custom operations to documents.
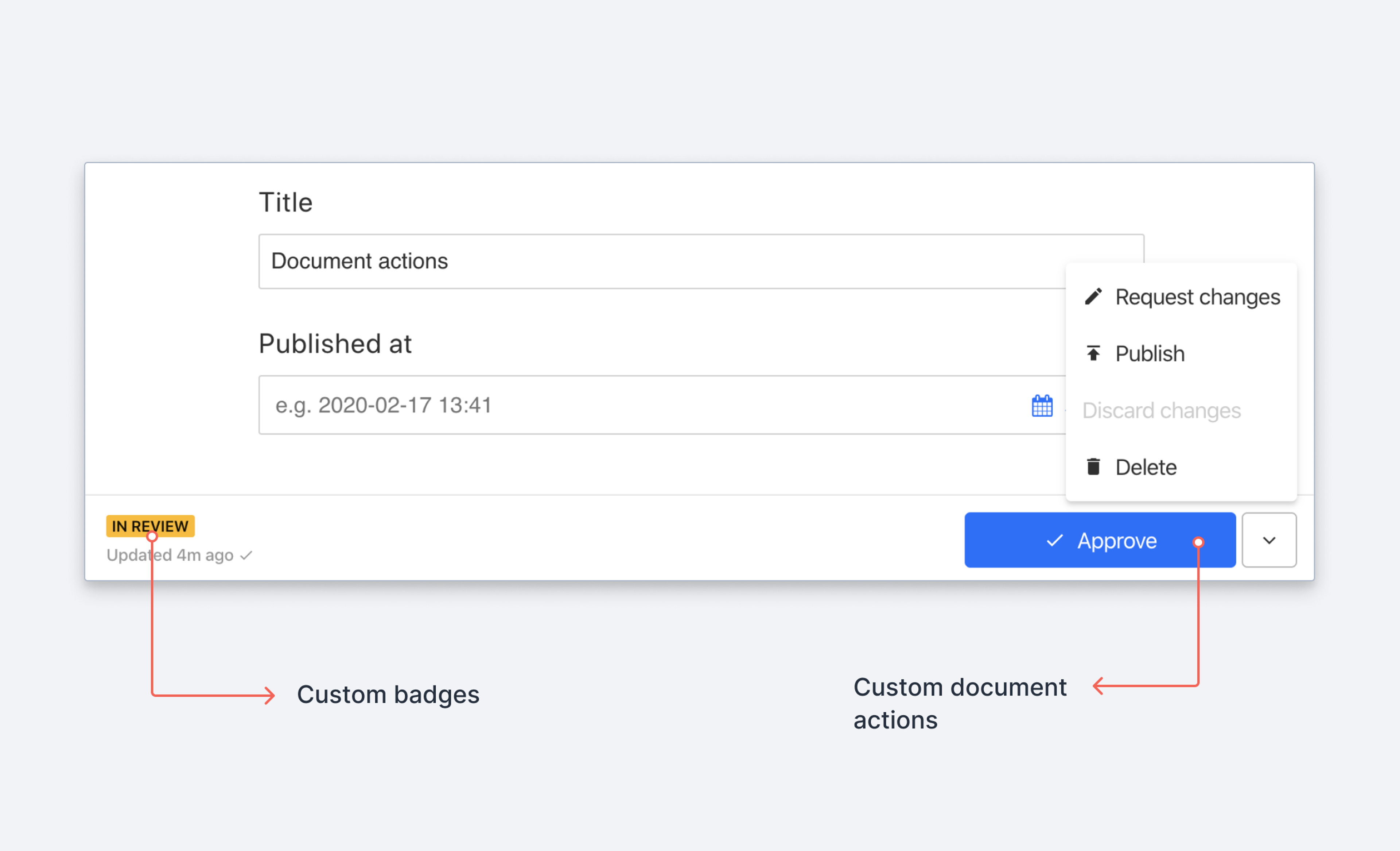
You can use the Document Actions API for Sanity Studio to customize and control operations that can be done to documents. When you create a custom action, it will be available in the actions menu in the document editor. You create custom actions by adding a DocumentActionComponent to the document.actions array of your workspace configuration.
Learn how to create custom workflows with the Document Actions API.
document.actions accepts either a static array of document action components or a callback function returning the same. When supplied with a static array, Sanity Studio will append your actions to the list of already existing actions.
Protip
Sanity Studio comes with a set of predefined document actions enabled that are helpful for manipulating documents. These are:
- Publish
- Unpublish
- Delete
- Duplicate
- Discard changes
- Restore to history state
You are free to swap any or all of these out with your own custom actions, or conditionally disable or enable them in your studio configuration.
import {CustomAction} from './actions'
export default defineConfig({
// ...rest of config
document: {
actions: [CustomAction],
},
})In contrast, when using the callback method, you will need to make sure you return the exact set of actions you want to register. Helpfully, the callback function receives the current array of registered action components as its first argument and a context object as its second and final argument.
import {HelloWorldAction} from './actions'
export default defineConfig({
// ... rest of config
document: {
actions: (prev, context) => {
// Only add the action for documents of type "movie"
// for other types return the current array of actions as is
return context.schemaType === 'movie' ? [HelloWorldAction, ...prev] : prev;
},
},
})Callback context properties
currentUserobject | CurrentUser
An object containing information about the currently logged in user
schemaTypestring
Schema type of the current document
datasetstring
Name of the dataset
projectIdstring
Unique ID of the project
getClientfunction
Returns a configured SanityClient
documentIdstring
ID of the document
schemaobject | Schema
The schema registry of your project. Use `schema.get("schemaTypeName") to retrieve any schema by name.
Example
document: {
actions: function (prev, context) {
console.log('context: ', context);
return prev.map((originalAction) => (originalAction.action === 'publish' ? HelloWorldAction : originalAction));
}
},Document Action components
This table describes the values a document action component receives as properties (DocumentActionProps):
Properties
idstring
The current document’s
id.typestring
The schema type of the current document.
draftSanityDocument
The draft document (e.g. unpublished changes) if any.
Returns
nullif there are no unpublished changes.publishedSanityDocument
The version of the document that is currently published (if any).
Returns
nullif the document isn't published.liveEditboolean
Whether the document is published continuously (live) or not. liveEdit-enabled documents skip the draft workflow. This is not to be confused with the Live Content API, which handles how published changes are handled by queries.
Identifying built-in actions
Built-in document action components have an optional action property that identifies which built-in action they represent. Use this to selectively replace or extend a specific action:
The action property uses values like 'publish', 'delete', 'duplicate', 'unpublish', 'discardChanges', and 'restore'. Custom actions don't have this property unless you set it.
Document Action description
Every Document Action component must return either null or an action description object (DocumentActionDescription). An action description describes the action state that can be used to render action components in different render contexts (e.g. in a toolbar, as a menu item, etc.). This table describes the different properties of an action description object.
Requiredlabelstring
This is the action label. If the action is displayed as a button, this is typically what becomes the button label.
RequiredonHandlevoid
This allows the action component to specify a function that gets called when the user wants the action to happen (e.g. the user clicked the button or pressed the keyboard shortcut combination). The implementation of the
onHandlemust either make sure to start the dialog flow or to execute the operation immediately.iconReact Element
In render contexts where it makes sense to display an icon, this will appear as the icon for the action. Default is
nulldisabledboolean
This tells the render context whether to disable this action. Default is
false.shortcutstring
A keyboard shortcut that should trigger the action. The keyboard shortcut must be compatible with the format supported by the is-hotkey-package.
titlestring
A title for the action. Depending on the render context this will be used as tooltip title (e.g. for buttons it may be passed as the title attribute). Default is
null.dialogConfirmDialog | PopOverDialog | ModalDialog
If this is returned, its value will be turned into a dialog by the render context. More about dialog types below. Default is
null.groupArray<'default' | 'paneActions'>
Allow users to specify whether a specific document action should appear in the footer ("default") or in the document's context menu ("paneActions").
toneButtonTone
Allows changing the tone of the action when displayed.
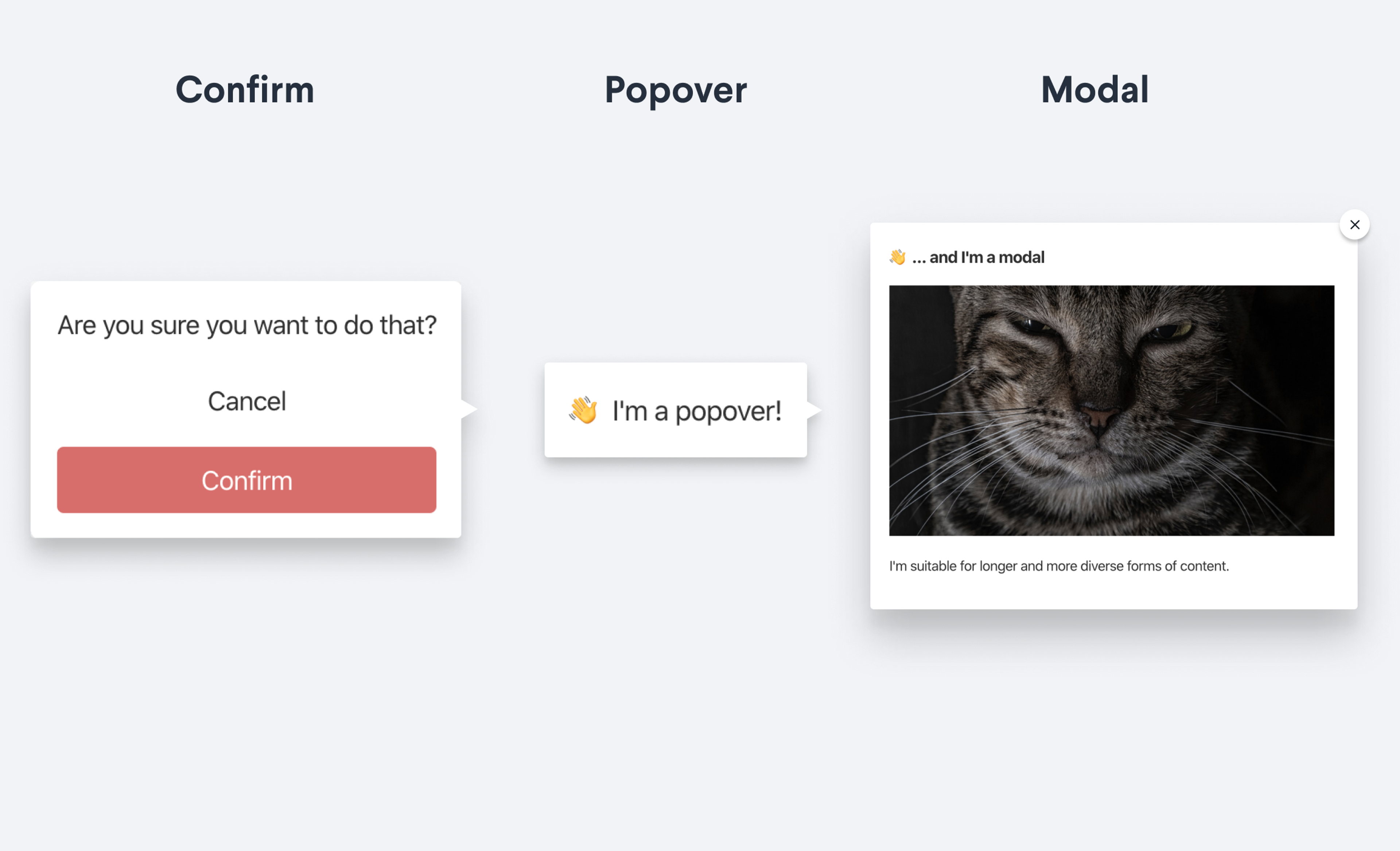
Document Action dialog types
Dialogs can notify and inform users about the outcome of an action, or they can collect confirmation before executing the action. You can define the following dialog types:
confirm
This tells the render context to display a confirm dialog. See the DocumentActionConfirmDialogProps reference for the full type definition.
Properties
typestring
Must be
confirm.colorstring
Support the following values
warning,success,danger,info.messagestring | React.ReactNode
The message that will be shown in the dialog.
onConfirmfunction
A function to execute when the the user confirms the dialog.
onCancelfunction
A function to execute when the user cancels the dialog.
Example
export function ConfirmDialogAction() {
const [dialogOpen, setDialogOpen] = React.useState(false)
return {
label: 'Show confirm',
onHandle: () => {
setDialogOpen(true)
},
dialog: dialogOpen && {
type: 'confirm',
onCancel: () => {
setDialogOpen(false)
},
onConfirm: () => {
alert('You confirmed!')
setDialogOpen(false)
},
message: 'Please confirm!'
}
}
}popover
This will display the value specified by the content property in a popover dialog (DocumentActionPopoverDialogProps). The onClose property is required, and will normally be triggered by click outside or closing the popover.
Example
export function PopoverDialogAction() {
const [dialogOpen, setDialogOpen] = React.useState(false)
return {
label: 'Show popover',
onHandle: () => {
setDialogOpen(true)
},
dialog: dialogOpen && {
type: 'popover',
onClose: () => {
setDialogOpen(false)
},
content: "👋 I'm a popover!"
}
}
}dialog
This will display the value specified by the content property in a dialog window (DocumentActionModalDialogProps). The onClose property is required.
Example
export function ConfirmDialogAction() {
const [dialogOpen, setDialogOpen] = React.useState(false)
return {
label: 'Show confirm',
onHandle: () => {
setDialogOpen(true)
},
dialog: dialogOpen && {
type: 'dialog',
onClose: () => {
setDialogOpen(false)
},
content: <div>
<h3>👋 ... and I'm a dialog</h3>
<img src="https://source.unsplash.com/1600x900/?cat" style={{width: '100%'}}/>
<p>
I'm suitable for longer and more diverse forms of content.
</p>
</div>
}
}
}custom
This will display the value specified by the component property in a custom dialog window. The onClose property is required.
Example
import {Button, Card, Dialog, Stack, Text} from '@sanity/ui'
export function CustomDialogAction() {
const [dialogOpen, setDialogOpen] = React.useState(false)
const toggleOpen = () => setDialogOpen(state => !state)
return {
label: 'Custom modal',
tone: 'primary',
onHandle: toggleOpen,
dialog: {
type: 'custom',
component: open && (
<Dialog
header="Custom action component"
id="custom-modal"
onClickOutside={toggleOpen}
onClose={toggleOpen}
width={1}
footer={
<Stack padding={2}>
<Button onClick={toggleOpen} text="Close" />
</Stack>
}
>
<Card padding={5}>
<Text>This dialog is rendered using a custom dialog component.
</Text>
</Card>
</Dialog>
),
}
}
}